The global energy landscape is changing rapidly, and Albania is no exception. With rising energy demands, aging infrastructure, and the need for sustainable solutions, the Albanian electrical sector is at a critical turning point. But within this challenge lies an opportunity: modernization, digitization, and green energy investment could turn Albania into a regional leader in renewable energy and smart grid technology.
Current State of Albania’s Electrical Grid
Albania’s energy system is heavily dependent on hydropower, which accounts for over 95% of domestic electricity production. While this makes the country one of the greenest in Europe in terms of production, it also makes the system vulnerable to droughts, seasonal variability, and climate change.
- TSO (OST): The transmission operator is modernizing infrastructure but still struggles with aging assets and peak load management.
- DSOs (like OSHEE) are dealing with high levels of technical and non-technical losses—among the highest in Europe.
The Push Toward Renewables and Solar
Albania has enormous untapped potential in solar and wind energy. In the last two years:
- Government has announced solar tenders and supported small-scale PV installations.
- Several solar parks are under construction or in planning phases.
- Households and businesses are beginning to invest in rooftop solar systems thanks to new incentives.
However, grid integration remains a challenge. Without smart infrastructure, adding large amounts of solar could destabilize the system.
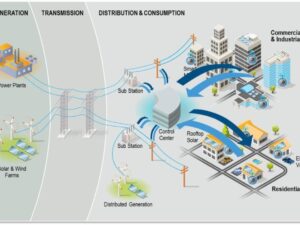
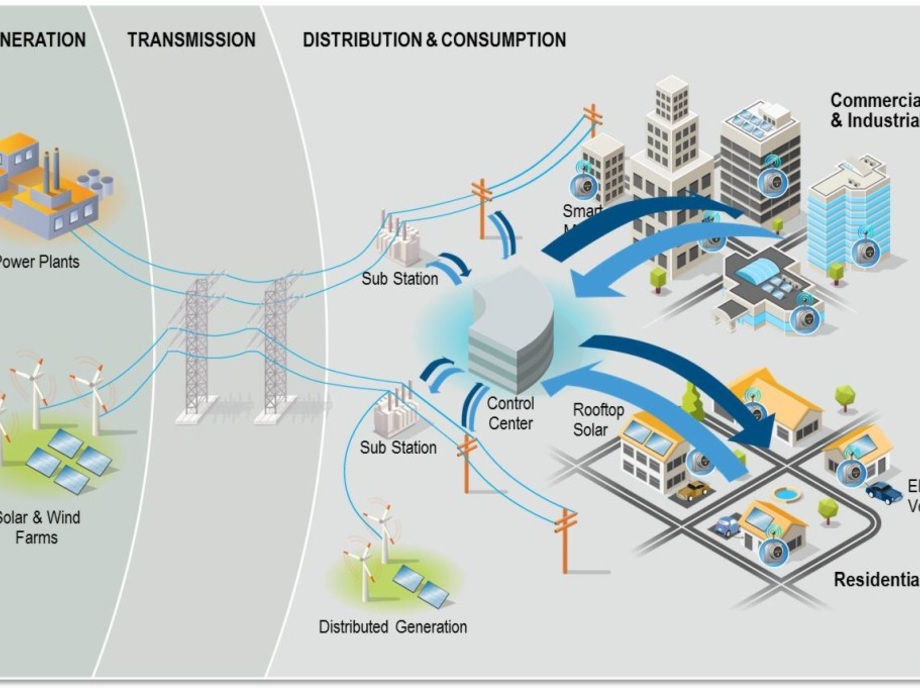
What’s Missing? Smart Grids and Energy Storage
For Albania to truly modernize, two technologies are essential:
Smart Grid Technology
- Real-time monitoring and data-driven decision making
- Smart meters to track and manage usage
- Predictive maintenance to reduce outages
Energy Storage
- Battery systems can balance fluctuations in hydropower and solar generation
- Opens the door to energy independence and microgrid deployments
Investment in these areas is low, but EU-backed funds and private investments are growing.
Digitization and Automation in the Sector
Just like other industries, the electrical sector is entering the Industry 4.0 era:
- SCADA systems are being upgraded in transmission and distribution stations.
- AI and IoT are being tested for fault detection, load forecasting, and remote control.
- Mobile apps for billing and outage reporting are improving customer experience.
However, skilled labor and cybersecurity remain major concerns.
Albania’s Role in the Regional Energy Market
With planned interconnections with North Macedonia, Kosovo, and Italy, Albania could become an energy hub for the Western Balkans. Projects like the Trans-Balkan Electricity Corridor aim to enhance cross-border energy trade and grid stability.
Challenges Ahead
- High technical losses (up to 20% in some areas)
- Regulatory bottlenecks for renewables
- Dependence on imports during dry seasons
- Slow pace of infrastructure upgrades
The Road Forward
To ensure energy security and sustainability, Albania needs to:
- Invest in smart grids, AI-powered systems, and storage solutions
- Modernize old substations and expand digital monitoring
- Support private solar and wind projects with stable feed-in tariffs or net metering
- Collaborate regionally to stabilize cross-border flows
The Albanian electrical sector is standing at a crossroads. With the right mix of policy, technology, and investment, the country can not only secure its own energy future but also become a clean energy exporter in the Balkans.