Off-grid solar power systems are an increasingly popular solution for individuals and families seeking energy independence, lower utility costs, and greater sustainability. Whether you live in a remote area, want a backup energy source, or simply aim to reduce your reliance on traditional power companies, building a reliable off-grid solar system is a powerful step forward.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know—from the core components of an off-grid system to the benefits and practical tips for implementation.
Why Go Off-Grid?
1. Energy Independence
Off-grid systems allow you to generate and store your own electricity, completely independent from utility companies. This makes them ideal for areas with unreliable grid power, or for those who want full control over their energy supply.
2. Cost Savings Over Time
Although the initial installation cost can be significant, you eliminate monthly electricity bills and can avoid rising energy prices. Over the long run, the savings can be substantial.
3. Sustainability
Solar energy is clean, renewable, and helps reduce your carbon footprint. By going off-grid, you’re actively contributing to a greener planet.
4. Reliability During Outages
An off-grid system equipped with battery storage can provide continuous power even during blackouts, giving you peace of mind in emergencies.
Core Components of an Off-Grid Solar Power System
Building a dependable off-grid system starts with understanding its key components:
1. Solar Panels
These capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. The number and size of panels you need depend on your energy usage and location.
2. Charge Controller
A charge controller regulates the voltage and current from the solar panels to the batteries. It protects your battery bank from overcharging or discharging, extending battery life.
3. Battery Bank
Batteries store the energy produced by the panels for use during the night or cloudy days. Lithium-ion batteries are increasingly preferred for their efficiency and longer lifespan.
4. Inverter
Inverters convert stored DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which is required to power most home appliances.
5. Backup Generator (Optional)
In areas with limited sunlight, a generator can be used as a backup to charge batteries when solar production is insufficient.
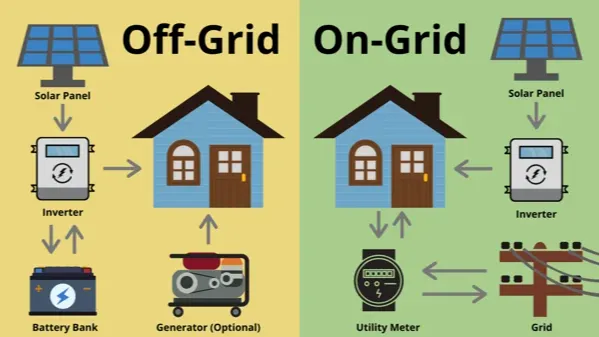
Off-Grid vs. On-Grid: Key Differences
| Feature | Off-Grid System | On-Grid System |
| Grid Connection | No | Yes |
| Energy Storage | Required (battery bank) | Optional |
| Power Outage Resilience | Unaffected by grid outages | Susceptible to outages |
| Energy Bills | No monthly utility bills | Monthly bills persist |
| Energy Surplus | Stored in batteries | Fed back to the grid (net metering) |
How to Plan and Build Your Off-Grid Solar System
Step 1: Assess Your Power Needs
Calculate your daily energy consumption by listing all appliances and their wattage. This helps determine the size of your system.
Step 2: Choose the Right Location
Install solar panels in areas with maximum sunlight exposure—typically a south-facing roof or an open yard.
Step 3: Select High-Quality Components
Invest in reliable panels, batteries, and inverters. Cheap components often result in system failures or inefficient performance.
Step 4: Install the System Safely
If you have electrical experience, you may choose to do the installation yourself. Otherwise, consult a licensed solar installer to ensure safety and compliance with local codes.
Step 5: Monitor and Maintain
Use a solar monitoring system to track performance. Regularly clean panels, check battery levels, and inspect wiring for long-term reliability.
Tips for a Successful Off-Grid Setup
- Oversize your battery bank for extended periods of low sunlight.
- Include surge protectors to safeguard electronics during voltage spikes.
- Plan for seasonal variations in solar production—especially in winter.
- Consider hybrid systems with both solar and generator inputs for flexibility.
Building a reliable off-grid solar system offers the freedom to live sustainably and securely, without dependence on the traditional power grid. With careful planning and quality components, you can enjoy uninterrupted power, financial savings, and a reduced environmental impact.
Whether you’re powering a cabin, tiny home, or full residence—off-grid energy gives you the tools to take control of your power future.